From reactive inspection to predictive intelligence
Welding quality has traditionally depended on post-process inspection – visual checks, ultrasonic tests, and rework once a defect is already present. Artificial intelligence is changing that model. By turning real-time process data into predictive insight, AI now allows fabricators to detect and prevent welding defects before they occur.
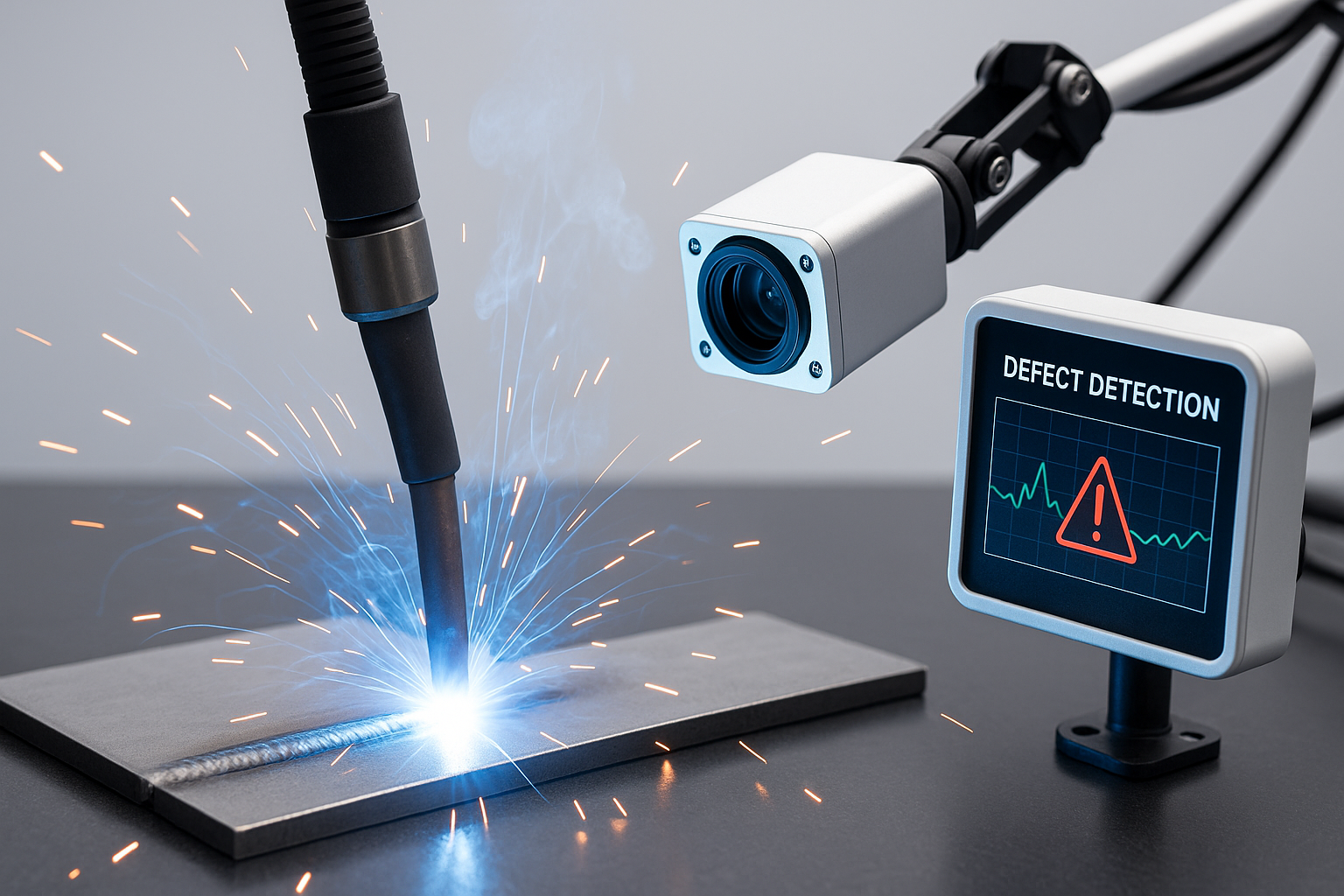
In sectors like automotive, heavy fabrication, and energy, AI systems monitor variables such as current, voltage, arc length, and torch angle across every weld. These models recognize subtle deviations that signal porosity, cracking, or lack of fusion – enabling immediate corrections rather than costly scrap later on.
This shift from reactive to predictive control represents one of the most practical and measurable benefits of industrial AI today. This same shift toward trust in predictive automation mirrors what’s happening in CNC programming – as explored in our feature on AI machining assistants.
Real-time monitoring: when data becomes foresight
The new generation of welding systems combines high-speed cameras, infrared sensors, and acoustic emission monitoring with machine-learning models trained on thousands of weld cycles.
Every arc, spark, and sound pattern contributes to a growing data set that helps AI distinguish between “normal” process noise and an early sign of defect formation.
When the algorithm senses instability – for example, inconsistent bead shape or spatter pattern – it alerts the operator or robotic controller instantly. This gives manufacturers a critical window to adjust parameters like gas flow, travel speed, or torch distance before the defect forms.
For many shops, the outcome is measurable: higher first-pass yield, reduced inspection time, and fewer production stops.
Closed-loop optimization: AI as the welding co-pilot
Advanced systems go a step further by feeding this intelligence back into the process.
Instead of waiting for human input, the AI can automatically fine-tune settings in real time – maintaining the perfect balance of current, voltage, and wire feed rate as material or environmental conditions change.
This “closed-loop” approach is becoming the foundation of autonomous welding control. The system learns continuously from every job, building a model of ideal parameters that adapts across materials, joint types, and thicknesses. The result is not just fewer defects, but a process that improves with every weld.
Practical adoption for fabricators
While predictive welding may sound complex, implementation is increasingly straightforward.
Sensor kits and vision modules can retrofit onto standard MIG, TIG, or laser welding equipment, sending data to cloud-based analytics platforms that require little specialist setup.
This democratizes the technology, making AI defect detection accessible for small and mid-size shops – not just large OEMs.
Manufacturers adopting these systems report significant reductions in rework and downtime, along with stronger documentation trails for quality assurance and traceability.
Choosing where data is processed – locally or in the cloud – plays a key role in responsiveness, as explored in Cloud vs Edge AI in the smart factory.
FAQ
How AI Detects Welding Defects Before They Happen?
AI analyses data from cameras, sensors, and electrical signals to identify abnormal patterns in temperature, voltage, or bead geometry. When a deviation appears, the system predicts a potential defect and can alert the operator or adjust parameters automatically.
What types of welding defects can AI prevent?
Common issues include porosity, undercutting, cracking, incomplete fusion, and spatter formation. By recognizing the process trends that lead to these defects, AI can intervene before they occur.
Can existing welding machines be upgraded with AI?
Yes. Many AI inspection systems are modular and can retrofit onto existing TIG, MIG, or laser welding setups. They connect via standard sensors and integrate with cloud or edge analytics platforms.
Is AI welding inspection only for large manufacturers?
No. Scalable hardware and subscription-based software make it accessible to small and mid-size fabricators. Even a single automated cell can benefit from predictive monitoring.
What is the ROI of AI-based defect detection?
Typical gains include reduced scrap rates, faster inspection cycles, and improved first-pass yield – often resulting in payback within 12–18 months depending on production volume.