For decades, writing CNC programs meant mastering complex syntax and carefully structuring every line of code. Now, a new shift is unfolding in workshops and digital manufacturing environments worldwide – a move from code to conversation.
From Code to Conversation
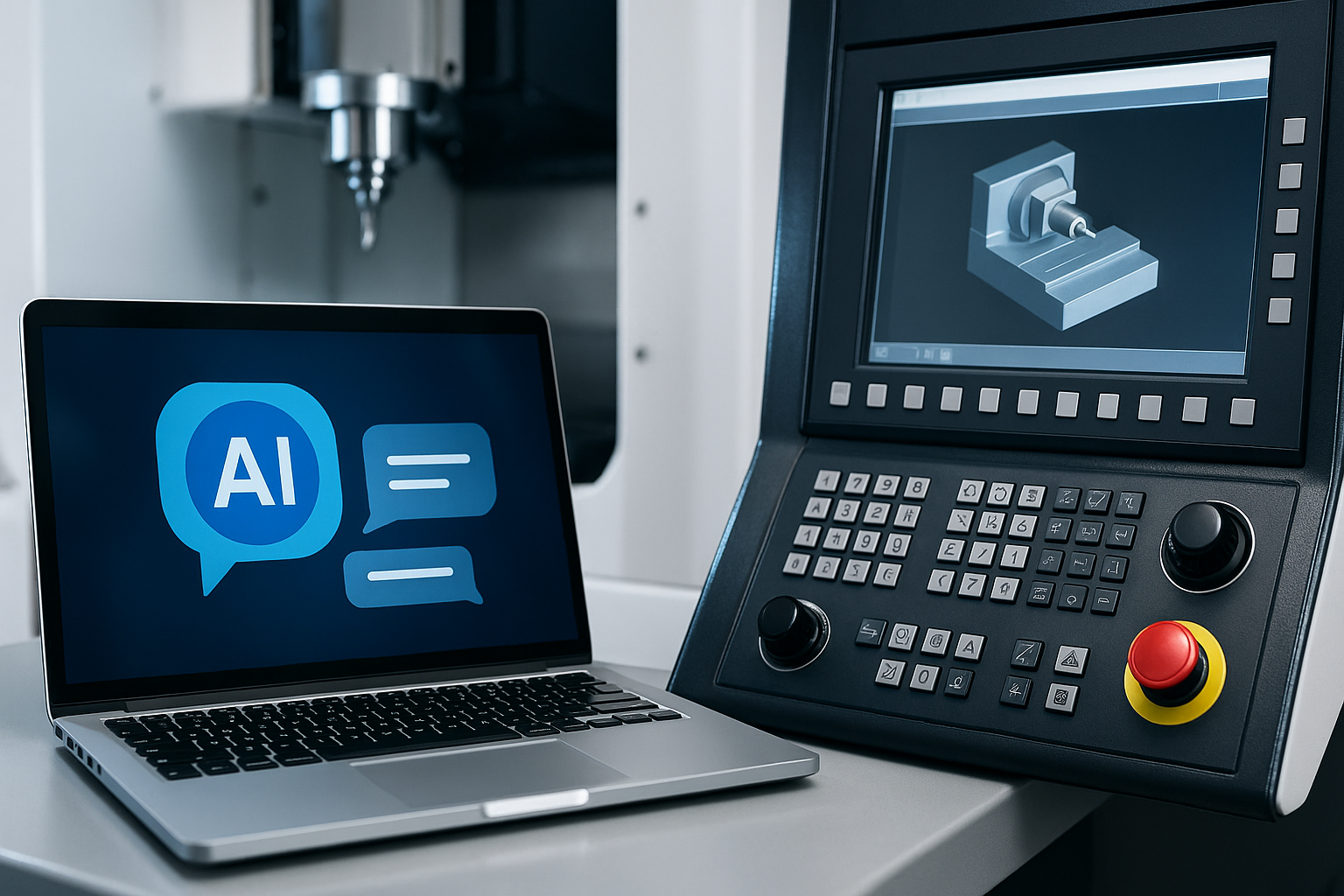
Conversational programming replaces traditional manual coding with AI systems that understand natural language. Instead of defining coordinates or commands, an operator can describe intent – such as “mill a pocket five millimetres deep” – and the system generates the corresponding program automatically.
This marks a major change in how manufacturing teams interact with machines. It turns programming from a technical exercise into a guided collaboration, where the AI handles geometry, speeds, feeds, and safety validation while the human defines the goal.
👉 AI Machining Assistants: Are Programmers Finally Ready to Trust the Algorithm?
The Role of Chatbots in Manufacturing
Conversational programming doesn’t stop at the CNC console. Chat-based interfaces are beginning to assist with tool selection, process optimisation, and workflow automation across connected manufacturing environments.
Operators can type or speak commands, ask for simulation checks, or recall previous job data – all through simple dialogue. The result is faster setup, reduced manual input, and improved repeatability from one job to the next.
As AI models continue to learn from production data, these conversational systems are becoming more context-aware, understanding intent and recognising recurring part geometries or materials without explicit instruction.
👉 Edge AI in Metal Factories: Why Local Processing Is Beating the Cloud
Why Conversational Programming Matters
1. Closing the Skills Gap
With experienced programmers in short supply, conversational systems allow newer operators to complete complex setups using natural language instead of advanced code.
2. Speed and Efficiency
AI-driven interaction shortens programming cycles, automates repetitive tasks, and helps standardise best practices across teams.
3. Fewer Errors, Safer Output
By interpreting intent and validating toolpaths automatically, conversational systems minimise syntax mistakes and reduce risk before a program ever reaches the machine.
4. Human–Machine Collaboration
Rather than replacing expertise, these systems enhance it – allowing programmers to focus on creative problem-solving while the AI manages the technical translation.
The Future: Voice-Driven Manufacturing
Voice control and conversational AI will soon merge with connected factory systems, enabling real-time adjustments, predictive optimisation, and fully adaptive machining environments. Operators may one day walk through a cell and simply say, “Run the next batch with a slower spindle speed,” and the change will be applied instantly.
Conversational programming is not just a convenience – it’s the foundation of a new era of human-machine communication that will make manufacturing faster, smarter, and more intuitive.versation.





One Comment