The Core of Every Machine
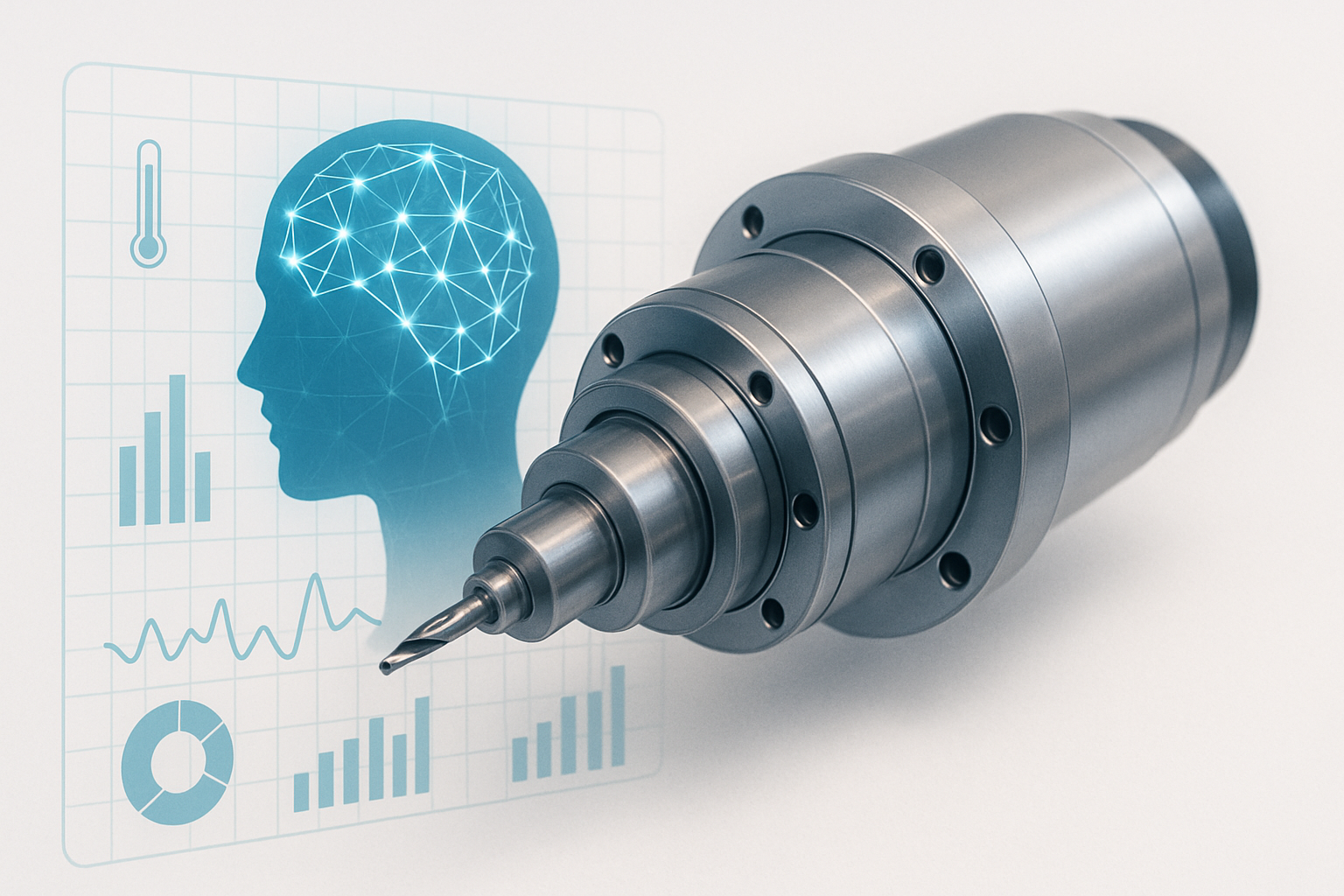
In any CNC or machining centre, the spindle is the beating heart – the component that defines speed, precision, and uptime. When a spindle goes down, production halts, costs soar, and delivery schedules slip. That’s why predictive maintenance for the spindle is becoming one of AI’s most valuable use-cases on the shop floor.
Modern AI models can now detect subtle vibration, temperature, and load anomalies long before a technician hears or feels them. Instead of relying on fixed maintenance intervals, AI-powered monitoring allows factories to act only when data shows an actual risk – saving both downtime and parts.
From Reactive to Predictive
Traditional maintenance cycles rely on operator intuition or scheduled checks. But spindle wear is rarely linear – tool balance, coolant flow, and even micro-vibrations can accelerate failure unpredictably.
AI changes that equation. By learning from thousands of hours of spindle telemetry, algorithms can build signatures of “normal” versus “abnormal” behaviour. When that baseline drifts, the system raises an alert – sometimes days before damage begins.
For example, accelerometer data can reveal minute changes in bearing resonance. AI then correlates this with motor current, temperature, and load to predict when performance is about to degrade. The outcome: early intervention, fewer rebuilds, and higher spindle-life ROI.
The Business Case: Uptime and Payback
In high-value machining – aerospace, medical, precision die-mould – a single unplanned spindle failure can cost tens of thousands in lost productivity. Predictive maintenance solutions typically pay for themselves after avoiding just one such incident.
When integrated with MES or ERP systems, these models also feed real-time performance dashboards. Maintenance can be scheduled automatically during idle windows rather than interrupting production. The result is measurable improvement in OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures), and operator trust.
👉 Related reading: AI Machining Assistants: Are Programmers Finally Ready to Trust the Algorithm?
👉 Also read: Edge AI in Metal Factories: Why Local Processing Is Beating the Cloud
The Next Layer: Spindle Digital Twins
The newest development is digital-twin modelling – virtual replicas of the spindle that evolve with each cycle.
AI doesn’t just flag anomalies; it simulates them. Engineers can run “what-if” scenarios to understand how a misaligned bearing or unbalanced tool would affect vibration signatures.
When paired with cloud-based service analytics, OEMs gain fleet-wide insight. A single spindle’s data can improve the design of the next generation. For machine builders, that’s a new service model: condition-based contracts instead of reactive warranty claims.
Real‑Time Digital Twin Models for Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing Systems
Integration Without Complexity
The good news for smaller shops: implementing predictive maintenance no longer requires massive investment. Compact sensors, edge AI gateways, and plug-in software modules can retrofit existing spindles.
Some CNC controls even come pre-equipped with vibration analytics channels, allowing AI models to run natively. These on-board systems filter noise and transmit only meaningful patterns to the cloud, protecting bandwidth while ensuring privacy of proprietary machining data.
What’s Coming Next
The “sweet spot” for AI in predictive maintenance lies at the intersection of reliability, cost, and transparency. As spindle systems become smarter, operators will see less unplanned downtime and more insight into component life.
Expect next-generation platforms to combine spindle analytics with tool condition monitoring, coolant flow, and part-quality feedback. The goal isn’t just to predict failure – it’s to keep the entire machining ecosystem continuously optimised.
Final Thoughts
AI-driven spindle maintenance is no longer a luxury feature; it’s fast becoming standard across competitive machining operations. The technology’s ability to forecast wear, extend life, and reduce cost positions it as one of the most practical and immediate returns from industrial AI adoption.
For manufacturers, it’s a simple proposition: protect the spindle, and you protect the business.
FAQs: Predictive Maintenance for the Spindle
1. What is predictive maintenance for CNC spindles?
Predictive maintenance uses AI to analyse spindle vibration, temperature, and load data to detect wear before failure occurs. It replaces fixed service intervals with data-driven alerts so maintenance happens only when needed.
2. How does AI predict spindle failure?
AI models learn normal vibration and current signatures from sensor data. When these patterns deviate – even slightly – the system flags potential bearing wear, imbalance, or lubrication issues before they escalate into costly downtime.
3. What data is needed for predictive maintenance?
Most systems rely on accelerometer (vibration), thermal, and current-load data from the spindle. Edge AI filters and processes these signals locally, sending only the relevant insights to the cloud or control dashboard.
4. Can older machines be retrofitted with AI monitoring?
Yes. Affordable sensor kits and compact edge gateways can retrofit older spindles. Many CNCs already have analogue input channels that can feed the data directly into predictive algorithms.
5. What’s the ROI of spindle predictive maintenance?
Avoiding just one unplanned spindle failure can offset the entire system cost. Users typically report 20–40% fewer breakdowns and longer spindle life – improving uptime, tool life, and scheduling efficiency.
6. What role do digital twins play?
A spindle digital twin is a virtual model that mirrors the real spindle’s behaviour. It helps engineers simulate wear conditions, refine maintenance thresholds, and improve future spindle designs using real production data.
7. Which industries benefit most?
Aerospace, automotive, and precision mould manufacturers gain the most – where downtime is expensive and tolerances are tight. However, any multi-shift shop can benefit from higher uptime and reduced maintenance cost.
8. Is cloud connectivity required?
Not always. Edge AI now allows analytics to run directly on-site, protecting data privacy and reducing bandwidth costs. Cloud options are used mainly for fleet-wide analytics and remote diagnostics.