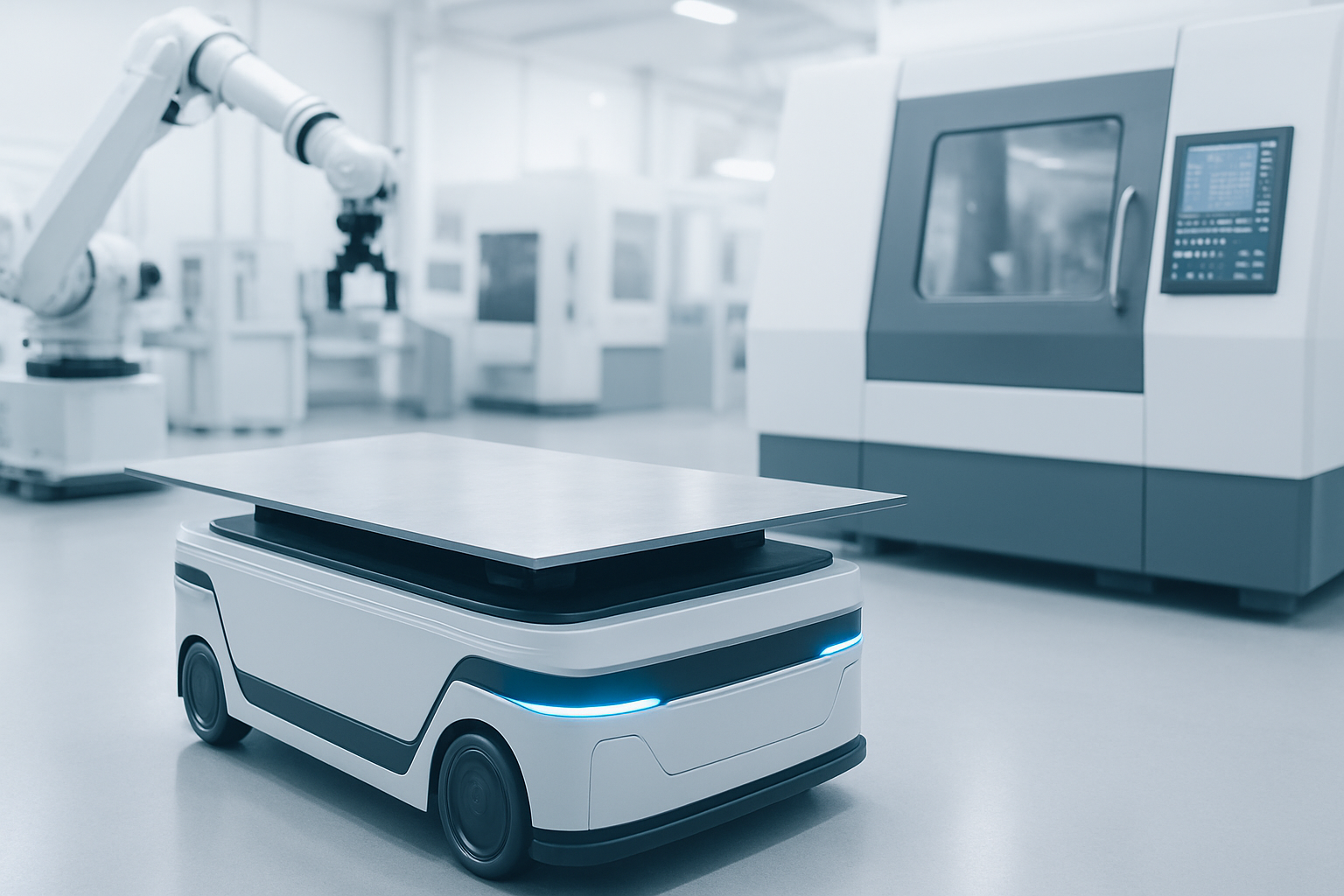
Material transport has always been a hidden bottleneck in metalworking. Sheets, cut parts, and semi-finished assemblies must move continuously between cutting, bending, welding, and finishing. Traditionally, this meant forklifts, pallet jacks, or operators pushing carts. Today, mobile robots in manufacturing are quietly reshaping that equation—bringing the same intelligence that transformed machining centers into the shop floor’s logistics.
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are no longer niche tools for warehouse giants. They are becoming standard equipment in metal fabrication shops, especially where lean operations and precision workflows demand that materials arrive at the right station at exactly the right time.
From Forklifts to AMRs: What’s Changed
For decades, internal logistics in fabrication relied on manual transport: skilled workers walking parts between machines, or forklift operators moving heavy pallets. These approaches worked, but they introduced three persistent issues:
- Labor dependency – moving material required time from workers who could otherwise be operating machines.
- Safety risks – forklifts and manual handling remain leading causes of shop floor accidents.
- Inefficiency – scheduling delays and waiting for transport add up to lost throughput.
Mobile robots manufacturing solves these pain points. Modern AMRs are:
- Self-navigating: Using LiDAR and 3D vision, they map the shop and adapt to changes in real time.
- Flexible: Unlike automated guided vehicles (AGVs) that need fixed paths, AMRs reroute dynamically.
- Connected: They integrate with MES/ERP systems, ensuring material flow matches live production data.
Why Metal Shops Are Turning to Mobile Robots
The adoption curve for mobile robots is accelerating in fabrication plants for three main reasons:
1. Labor Shortages and Cost Pressure
Skilled machinists and welders are already hard to find. Shops can’t afford to allocate them to pushing carts. Mobile robots cut wasted labor hours and let human talent focus on high-value operations.
2. Safety and Compliance
OSHA reports that forklifts are involved in nearly 85 fatalities and 34,900 serious injuries annually in the U.S. (OSHA). By removing forklifts from routine transport, mobile robots reduce collision and lifting hazards.
3. Smart Factory Integration
With Industry 4.0 adoption, real-time production data is already flowing. Mobile robots extend that connectivity to logistics—turning transport into a data-driven, predictable process instead of an ad hoc task.
Applications in Metal Fabrication
The most common use cases for mobile robots in manufacturing shops include:
- Raw sheet delivery – AMRs deliver large sheet bundles to laser cutters without tying up forklifts.
- WIP transfer – moving bent parts from press brakes to welding stations.
- Tooling supply – autonomous delivery of dies, fixtures, and consumables to machines.
- Finished goods staging – transporting packed components to shipping areas.
In many shops, a fleet of just 2–3 robots can handle all intra-plant logistics—creating measurable ROI within 12–18 months.
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
Despite proven benefits, some fabricators hesitate to deploy AMRs. Common concerns include:
- Cost of entry – while unit prices have dropped, integration and mapping still require upfront investment.
- Shop floor complexity – tight aisles, mixed equipment, and heavy parts require robust navigation.
- Change management – operators must adapt to working alongside autonomous systems.
The key enabler is modular deployment. Leading suppliers allow shops to start with one or two robots, scaling as confidence and ROI grow. Integration with existing ERP/MES platforms is also becoming simpler, thanks to open APIs.
The Competitive Edge
Mobile robots won’t replace skilled fabricators—they amplify them. By removing the waste of manual material movement, shops can:
- Increase spindle utilization in CNC departments.
- Improve OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) in welding and bending lines.
- Shorten lead times, giving a competitive edge on delivery promises.
As global competition intensifies, shops that adopt mobile robots in manufacturing gain agility while reducing safety risks and labor costs. For many, it’s no longer a question of if, but when.





One Comment